TensorFlow Test
In just two years, Tensorflow™ has become one of the most popular libraries for deep machine learning. It is essential to achieve the highest possible performance while working on Tensorflow™ projects, same as with the development of any other software product.
One of the effective ways to increase the speed of calculations advised by Google advised is to avoid using a precompiled package of the Tensorflow™ library, and replace it with Tensorflow™ version compiled directly from the source code. Recently a study was conducted in order to test Google's proposed method where the same projects were launched using Tensorflow™ without the support of the CUDA® platform installed in three different ways:
- Using a precompiled package;
- Compiled directly from the source code without supporting CPU instructions;
- Compiled directly from the source code supporting CPU instructions (AVX, AVX2 and FMA, etc.).
Tensorflow™ library tests with support for the CUDA® platform were also conducted. Following test results were taken as benchmarks:
- Tests with real data. A network of the Inception-ResNet-v2 type was taken and trained to recognize the gender of people with help of the FaceScrub data set (http://vintage.winklerbros.net/facescrub.html).
- Synthetic tests from the official site of TensorFlow™. The neural network model is Inception v3 (https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/performance/measurement).
Tests were conducted on the server with the following configuration (www.leadergpu.com):
- GPU: NVIDIA® Tesla® P100 (16 GB)
- CPU: 2 x Intel® Xeon® E5-2630v4 2.2 GHz
- RAM: 128 GB
- SSD: 960 GB
- Ports: 40 Gbps
- OS: CentOS 7
- Python 2.7
- TensorFlow™ 1.3
Commands for installing Tensorflow™ without CUDA® support:
Installing Tensorflow™ from a precompiled package:
# pip install tensorflowInstalling Tensorflow™, compiled directly from the source code:
# git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow
# cd tensorflow
# git checkout r1.3
# ./configure-
for compilation without support for CPU commands:
# bazel build -c opt //tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package -
for compilation with support for CPU commands:
# bazel build -c opt --copt=-mavx --copt=-mavx2 --copt=-mfma --copt=-mfpmath=both --copt=-msse4.1 --copt=-msse4.2 //tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package bazel-bin/tensorflow/tools/pip_package/build_pip_package /tmp/tensorflow_pkg # pip install /tmp/tensorflow_pkg/1.3.0-cp27-cp27mu-linux_x86_64.whl
Tests on real data and synthetic data without the support of CUDA
Commands for starting a network for tests with real data:
# cd gender_net
# python download_data.py
# python convert_data_FS.py
# time python model_FS_mulGPU_v3.pyCommands for running tests with synthetic data:
# mkdir ~/Anaconda
# cd ~/Anaconda
# git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/benchmarks.git
# cd ~/Anaconda/benchmarks/scripts/tf_cnn_benchmarks
# python tf_cnn_benchmarks.py --devicecpu model --inception3 --batch_size 32 --data_format NHWC --num_batches 40
Testing Tensorflow™, installed from a precompiled package:
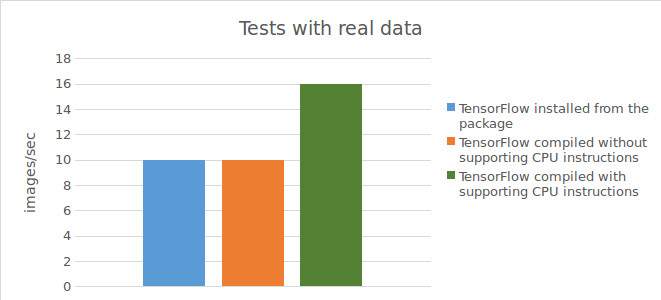
Result for tests with real data:
10 images / sec;
test script running time
= 20m55s.
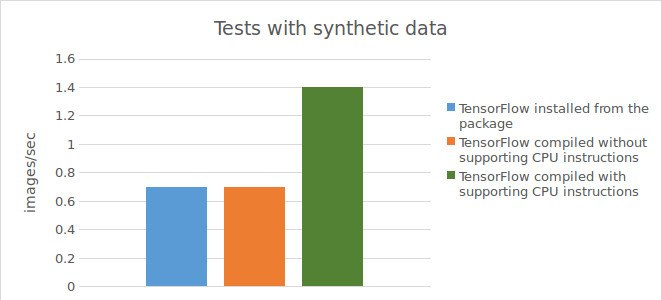
Result for tests with synthetic data:
0,73 images/sec;
test script running time
= 36m25s.
Testing Tensorflow™, compiled directly from the source code without the support of CPU instructions:
Result for tests with real data:
10 images/sec;
test script running time
= 20m55s.
Result for tests with synthetic data:
0,74 images/sec;
test script running time
= 36m21s.
Testing Tensorflow™, compiled directly from source code with support for CPU instructions:
Result for tests with real data:
15-16 images/sec;
test script running time
= 14m13s.
Result for tests with synthetic data:
1,44 images/sec;
test script running time
= 18m40s.
Below is a chart showing the tests results.
Commands for installing Tensorflow™ with CUDA® support:
Installing Tensorflow™ from a precompiled package:
# pip install tensorflowInstalling Tensorflow™, compiled directly from the source code:
# git clone https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow
# cd tensorflow
# git checkout r1.3
#./configure
# bazel build -c opt --copt=-mavx --copt=-mavx2 --copt=-mfma --copt=-mfpmath=both --copt=-msse4.1 --copt=-msse4.2 --config=cuda //tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package
bazel-bin/tensorflow/tools/pip_package/build_pip_package /tmp/tensorflow_pkg
# pip install /tmp/tensorflow_pkg/1.3.0-cp27-cp27mu-linux_x86_64.whlCommands for starting networks are similar to the commands from previous tests except for the command to run the script to start learning the network on synthetic data:
# python tf_cnn_benchmarks.py --num_gpus=1 --model inception3 --batch_size 32Tests on real data and synthetic data with support for CUDA
Testing Tensorflow™, installed from a precompiled package:
Result for tests with real data:
214 images/sec.
Result for tests with synthetic data:
126,33 images/sec.
Testing Tensorflow™, compiled directly from source code with support for CPU instructions:
Result for tests with real data:
215 images/sec.
Result for tests with synthetic data:
126,34 images/sec.
To summarize the results of the accomplished tests, the use of Tensorflow™ compiled directly from the source code (with support for CPU instructions) makes it possible to achieve significant increase in acceleration (1.5 times with real data and twofold with synthetic data) when performing calculations on the CPU. However, while working with GPU, the use of Tensorflow™, compiled directly from the source code, did not allow achieving any improvement in results compared to Tensorflow™, installed from the precompiled package.





